However, this article describes the basic explanation about the mechanism of T-helper (Th) cells disturbing the immune system, as well as the factors causing this imbalance.
What are Th1 and Th2?
T-helper cells (Th) are an important part of the immune system. They are lymphocytes that recognize foreign pathogens or normal tissues in autoimmune diseases. Cytokines are produced as a response. These Th cells are divided into subgroups:
Effect of Th Responses in Autoimmune Disease
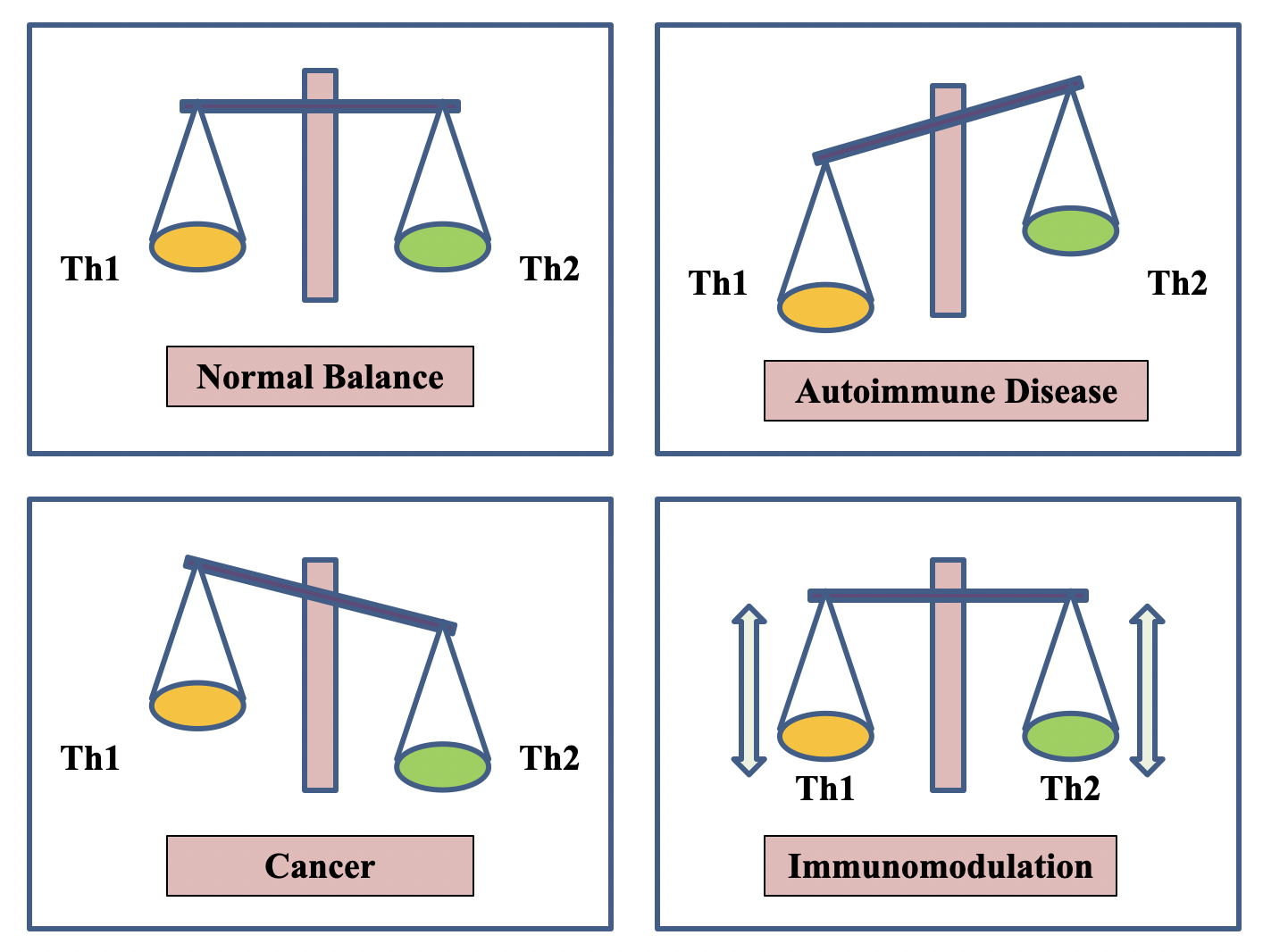
An alteration in Th1-Th2 balance causes various autoimmune diseases. This is described in the figure.
When the Th1 cells of the immune system are overactive, they can suppress the activity of Th2 and vice versa. This can be problematic, because these two components of the immune system function in a delicately balanced relationship. In the case of autoimmune disease, an imbalance can further the attack on healthy tissue, thereby worsening symptoms.
What are Th1 and Th2?
T-helper cells (Th) are an important part of the immune system. They are lymphocytes that recognize foreign pathogens or normal tissues in autoimmune diseases. Cytokines are produced as a response. These Th cells are divided into subgroups:
Th1 | Th2 |
Involved in “cell-mediated” immunity | Involved in “humoral-mediated” immunity |
Usually deals with infections by viruses and certain bacteria | Usually deals with infections by bacteria, toxins, and allergens |
Body’s first line of defense against pathogens that get inside our cells | Stimulating the production of antibodies in response to extracellular pathogens (those found in blood or other body fluids) |
Tend to be pro-inflammatory | Tend to be anti-inflammatory |
Involved in the development of organ-specific autoimmune disease | Involved in systemic autoimmune disease and other chronic conditions |
In a well-functioning immune system, both groups of these T helper cells work together to keep the system balanced. One side might become more active to eradicate a threat, then settling back to a balanced level.
Effect of Th Responses in Autoimmune Disease
An alteration in Th1-Th2 balance causes various autoimmune diseases. This is described in the figure.
When the Th1 cells of the immune system are overactive, they can suppress the activity of Th2 and vice versa. This can be problematic, because these two components of the immune system function in a delicately balanced relationship. In the case of autoimmune disease, an imbalance can further the attack on healthy tissue, thereby worsening symptoms.
Maintaining a balance between Th1 and Th2 immunological responses is paramount to healthy immune functionality.